InMAP Quickstart
About InMAP
InMAP is a multi-scale emissions-to-health impact model for fine particulate matter (PM2.5) that mechanistically evaluates air quality and health benefits of perturbations to baseline emissions. A main simplification of InMAP compared to a comprehensive chemical transport model is that it does so on an annual-average basis rather than the highly time-resolved performance of a full CTM. The model incorporates annual-average parameters (e.g. transport, deposition, and reaction rates) from the a chemical transport model. Grid-cell size varies as shown in Figure 1, ranging from smaller grid cells in urban areas to larger grid cells in rural areas. This variable resolution grid is used to simulate population exposures to PM2.5 with high spatial resolution while minimizing computational expense.
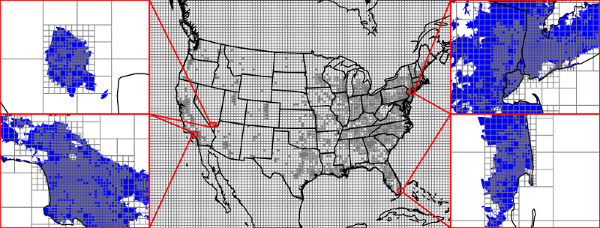 Figure 1: InMAP spatial discretization of the model domain into variable resolution grid cells. Center panel: full domain; outer panels: small sections of the domain centered on urban areas.
Figure 1: InMAP spatial discretization of the model domain into variable resolution grid cells. Center panel: full domain; outer panels: small sections of the domain centered on urban areas.
Getting InMAP
Go to releases to download the most recent release for your type of computer. For Mac systems, download the file with "darwin" in the name. You will need both the executable program and the input data ("evaldata_vX.X.X.zip"). All of the versions of the program are labeled "amd64" to denote that they are for 64-bit processors (i.e., all relatively recent notebook and desktop computers). It doesn't matter whether your computer processor is made by AMD or another brand, it should work either way.
Running InMAP
Make sure that you have downloaded the InMAP input data files:
evaldata_vX.X.X.zipfrom the InMAP release page, where X.X.X corresponds to a version number. The data files may need to be downloaded from a separate link included in the release information rather than directly from the release page.Create an emissions scenario or use one of the evaluation emissions datasets available in the
evaldata_vX.X.X.zipfiles on the InMAP release page. Emissions files should be in shapefile format where the attribute columns correspond to the names of emitted pollutants. The acceptable pollutant names areVOC,NOx,NH3,SOx, andPM2_5. Emissions units can be specified in the configuration file (discussed below) and can be short tons per year, kilograms per year, or micrograms per second. The model can handle multiple input emissions files, and emissions can be either elevated or ground level. Files with elevated emissions need to have attribute columns labeled "height", "diam", "temp", and "velocity" containing stack information in units of m, m, K, and m/s, respectively. Emissions will be allocated from the geometries in the shape file to the InMAP computational grid.Make a copy of the configuration file template and edit it if desired, keeping in mind that you will either need to set the
evaldataenvironment variable to the directory you downloaded the evaluation data to, or replace all instances of${evaldata}in the configuration file with the path to that directory. You must also ensure that the directoryOutputFileis to go in exists. Refer to the documentation here for information about other configuration options. The configuration file is a text file in TOML format, and any changes made to the file will need to conform to that format or the model will not run correctly and will produce an error.Run the program:
inmapXXX run steady --config=/path/to/configfile.tomlwhere
inmapXXXis replaced with the executable file that you downloaded. For some systems you may need to type./inmapXXXinstead. If you compiled the program from source, the command will just beinmapfor Linux or Mac systems andinmap.exefor Windows systems.The above command runs the model in the most typical mode. For alternative run modes and other command options refer here.
View the program output. The output files are in shapefile format which can be viewed in most GIS programs. One free GIS program is QGIS. By default, the InMAP only outputs ground-level, but this can be changed using the configuration file.
